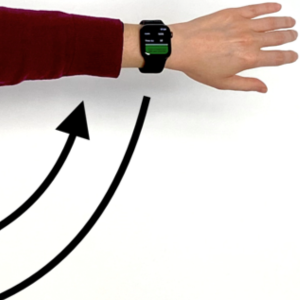
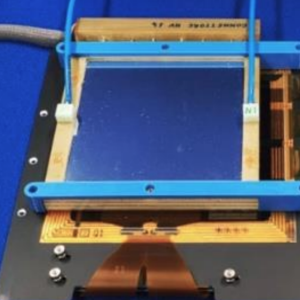
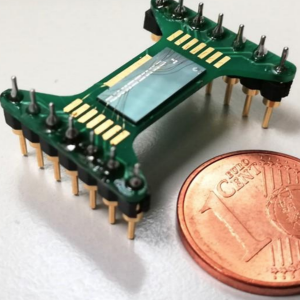
A brain stroke occurs when the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the brain is obstructed or when a blood vessel leaks or bursts. It is the second leading cause of death in Europe, and 60% of the survivors have different degrees of disability, with a socio-economic impact of the first magnitude for...
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.