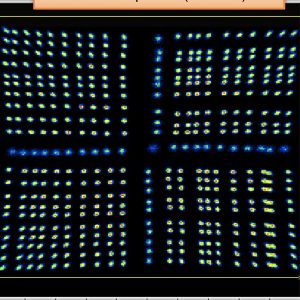
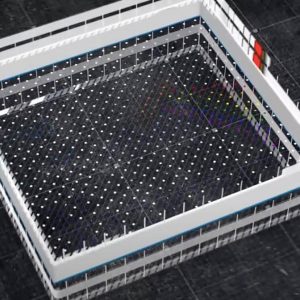
The recent technological breakthrough in cryo electron tomography (cryoET) opens to imaging, at close to atomic resolution, of macromolecular complexes in their native cellular context. This technique is seminal for a new field in Life Sciences referred to as cellular structural biology which is starting to shed light on how fine conformational states of protein...
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.